Branch and Bound
Similar to “Backtracking”
- a state-space tree is used to solve a problem (pruning tree 사용한다)
Different from “Backtracking”
- does not limit us to any particular way of traversing a tree (탐색하는데에, 방법제한이 없다.)
(backtrack에서는 recursion기반의 dfs가 중점적이다)
- is used only for optimization problems (bound값을 사용해야해서, 최적문제들만 사용가능함)
Step 1
computes a number (bound) at a node to determine whether the node is promising
(the number is a bound on the value of the solution
that could be obtained by expanding beyond the node )
bound 값 = 계속 node를 expanding해서 얻을 수 있는 최대 profit_bound 값!
Step 2
if the bound is no better than the value of the best solution found so far,
the node is non-promising
bound값이 예전 best 값보다 좋지 않는 경우 : non promising
6.1 The 0-1 Knapsack Problem
Best-First Search with Branch and Bound Pruning
(1)Basic Idea
(1) bound 사용법 : promising 결정하는 것보다 다음 node가 expand되는 것에 사용한다.
(2) priority queue 사용 : bound 기준으로 우선순위 큐를 사용한다.
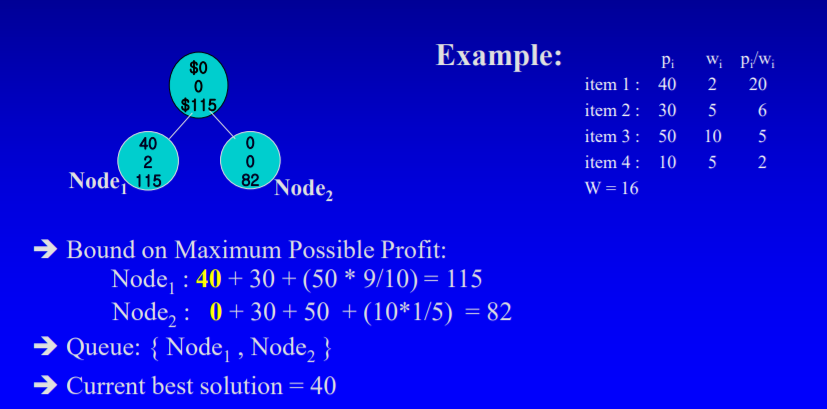
(2)[그림 예시]
1. 처음 상태

Node 0의 bound 값 계산한 뒤 queue에 넣는다
public static int knapsack3(int n, int[ ] p, int[ ] w, int W)
{
priority_queue_of_node PQ ; node u, v ;
int maxProfit ;
v.level = 0 ; v.profit = 0; v.weight=0 ; maxProfit = 0 ;
v.bound = bound(v) ;
PQ.enqueue(v) ;2. 두번째
Queue가 비어있지 않으면, 앞의 bound제일 큰 값의 node를 dequeue해서
dequeue node의 bound값이 현재 best profit보다 크면, expand한다 ( basic idea 1 : bound 사용법)
while( ! PQ.Empty() ){
v = PQ.dequeue() ;
if (v.bound > maxProfit) {
u.level = v.level + 1 ;
take care of the left child ;
take care of the right child ;
}왼쪽자식은 다음 w[i+1]의 profit을 포함하는 것
(1) 왼쪽자식 weight , profit
u.weight = v.weight + w[u.level] ;
u.profit = v.profit + p[u.level] ;(2) 왼쪽자식의 profit이 현재 best profit(maxProfit)보다 크면 update
if (u.weight<=W && u.profit > maxProfit)
maxProfit = u.profit ;(3) 큐 삽입 조건 : bound가 best profit보다 큰 경우
u.bound = bound(u) ;
if (u.bound > maxProfit)
PQ.enqueue(u) ;오른쪽자식은 포함하지 않는 것
u.weight = v.weight ;
u.profit = v.profit ;
u.bound = bound(u) ;
if ( u.bound > maxProfit)
PQ.enqueue(u) ;(3)code
public class node { int level ; int profit ; int weight ; int bound ; }
public static int knapsack3(int n, int[ ] p, int[ ] w, int W)
{
priority_queue_of_node PQ ; node u, v ;
int maxProfit ;
v.level = 0 ; v.profit = 0; v.weight=0 ; maxProfit = 0 ;
v.bound = bound(v) ;
PQ.enqueue(v) ;
while( ! PQ.Empty() ){
v = PQ.dequeue() ;
if (v.bound > maxProfit) {
u.level = v.level + 1 ;
take care of the left child ;
take care of the right child ;
}
}//왼쪽 자식 (node넣는 경우)
u.weight = v.weight + w[u.level] ;
u.profit = v.profit + p[u.level] ;
if (u.weight<=W && u.profit > maxProfit)
maxProfit = u.profit ;
u.bound = bound(u) ;
if (u.bound > maxProfit)
PQ.enqueue(u) ;
//오른쪽 자식 (node 안넣는경우)
u.weight = v.weight ;
u.profit = v.profit ;
u.bound = bound(u) ;
if ( u.bound > maxProfit)
PQ.enqueue(u) ;public static float bound(node u)
{
index j,k ; int totWeight ; float result ;
if (u.weight >= W) return 0 ;
else {
result = u.profit ;
j = u.level + 1 ;
totWeight = u.weight ;
while (j<=n && totWeight+w[j] <= W){
totWeight = totWeight + w[j] ;
result = result + p[j] ;
j++ ;
}
k = j ;
if (k <= n)
result=result+(W-totWeight)*p[k]/w[k];
return result ;
}
}6.2 The Traveling SalesPerson Problem
TSP는 leaf 노드를 찍어야 해를 구할 수 있다.
TSP는 자기 자신에서 모든 경로를 거쳐와서 자기 자신으로 돌아오는 경로 중 최단 경로.
[i1, i2, … , ik] : 1부터 k까지 2와 k-1를 거치는 경로를 말한다.
How to define how to compute the bound on each node?
- At the level k of the state space tree, each node corresponds to a state where (k+1) vertices have been visited.
k번째의 tree에서, 각 노드는 (k+1) 노드가 방문하는 노드에 일치한다.
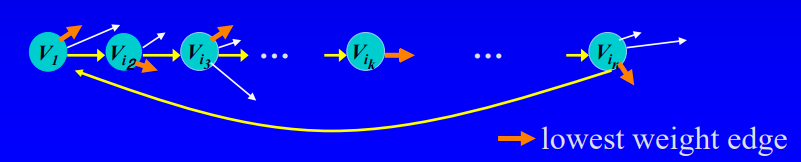
1. root 노드의 lower bound
= ∑ vm∈V (lowest weight of edge leaving vm)
: 각 노드에서의 경로 중 lowest weight edge를 고른 것.
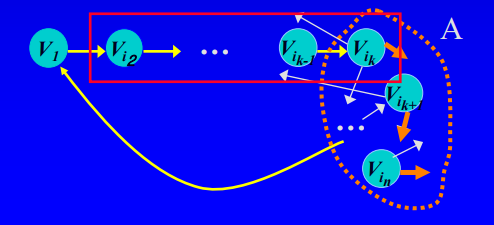
2. node [1, i2, ... , ik] ( 1 < k < n ) 의 lower bound
= sum of actual weight from V1 to Vk +
∑ vm∈A (lowest weight of edge leaving Vm excluding those to vertices i2, ..,ik and the edge from Vik to V1 )
where A = V – {V1,Vi2, ..,Vik-1}
= i~k는 지나온 node들 + 지나온 2~k node제외 + k에서 1로 가는 경로 제외
Example
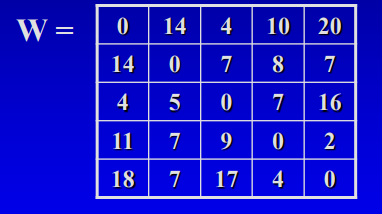
1. root node
root 노드의 lower bound
= ∑ vm∈V (lowest weight of edge leaving vm)
: 각 노드에서의 경로 중 lowest weight edge를 고른 것.
= 4 + 7 + 4 + 2 + 4 = 21
현재 우선순위큐에 node 0 ( root node) 들어있다.
best 값 (제일 작은 lower bound) 는 아직 정할 수 없다. best는 leaf node까지 가야 구할 수 있다.
public static number travel2(int n, number[ ] W, node optTour)
{
priority_queue_of_node PQ; node u, v ;
number minLength ;
PQ.initialize() ;
v.level = 0; v.path =[1]; minLength= ∞;
v.bound=bound(v);
PQ.enqueue(v) ;2. 두번째 ~ 리프 level 전
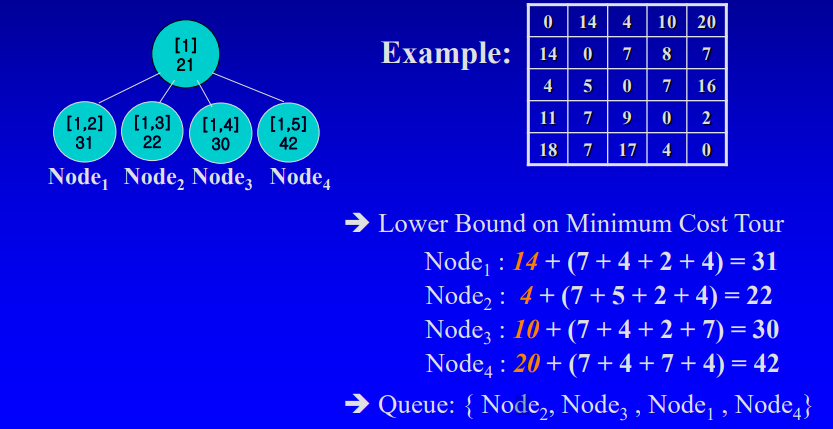
best는 구하지 못해도, node 0을 dequeue해 자식노드를 구할때, lower bound 값 순서대로 우선순위 큐에 넣는다.
while(! PQ.Empty() ) {
v = PQ.dequeue() ;
if v is promising // the bound of v < minLength
take_care_of_children ;
}
3. leaf 노드
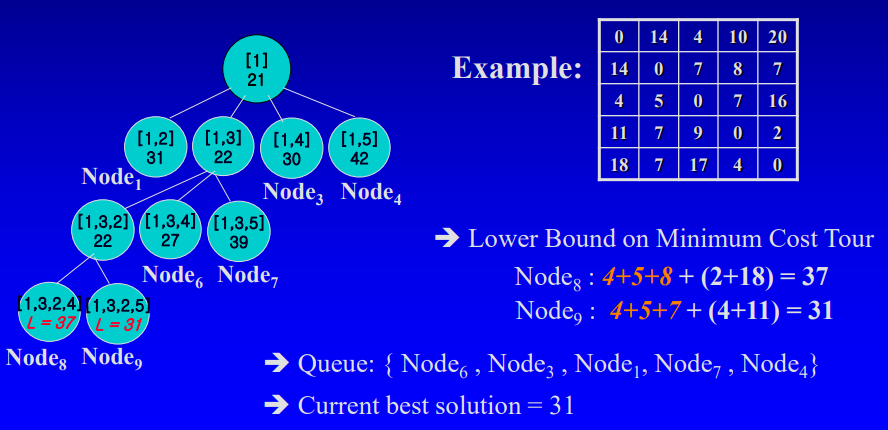
best 를 update 한다. 그리고 이제 best 값과 각 노드의 lower bound를 비교하여 best 보다 큰 노드들은 버린다.
code
public static number travel2(int n, number[ ] W, node optTour)
{
priority_queue_of_node PQ; node u, v ;
number minLength ;
PQ.initialize() ;
v.level = 0; v.path =[1]; minLength= ∞;
v.bound=bound(v);
PQ.enqueue(v) ;
while(! PQ.Empty() ) {
v = PQ.dequeue() ;
if v is promising // the bound of v < minLength
take_care_of_children ;
}take_care_of_children
u.level = v.level +1;
for (all i such that 2 ≤ i ≤ n && i not in v.path) {
u.path = v.path ; put i at the end of u.path;
if ( u.level == n-2 ) {
put index of only vertex not in u.path at the end of u.path ;
put 1 at the end of u.path;
if (length(u) < minLength) {
minLength = length(u) ; optTour = u.path ;
}
}
else {
u.bound = bound(u) ;
if (u.bound < minLength )
PQ.enqueue(u) ;
}for문 : k+1의 범위는 2~n이다. 지나온 경로를 제외한 node들.
u.level = v.level +1;
for (all i such that 2 ≤ i ≤ n && i not in v.path) {
u.path = v.path ; put i at the end of u.path;leaf node일때 : root는 level 0이다. 트리의 전체 level은 n-1이므로 n-2인 경우 leaf 노드.
if ( u.level == n-2 ) {
put index of only vertex not in u.path at the end of u.path ;
put 1 at the end of u.path;
if (length(u) < minLength) {
minLength = length(u) ; optTour = u.path ;
}
}만약 leaf node의 값이 best보다 작으면, best update한다.
leaf node 아닐 때 : best (minLength) 보다 작은 경우 큐에 넣는다.
else {
u.bound = bound(u) ;
if (u.bound < minLength )
PQ.enqueue(u) ;
}'programming language > Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Divide and Conquer 예제] 프로그래머스 Level3 네트워크 (0) | 2021.08.25 |
|---|---|
| [Divide and Conquer 예제] 프로그래머스 Level2 타겟넘버 (0) | 2021.08.25 |
| [Dynamic Programming 예제] 백준 12865 배낭문제 (0) | 2021.08.20 |
| [Backtracking 예제] 백준 9663 N-Queens (0) | 2021.08.19 |
| [Greedy Approach 예제] 백준 2839 설탕배달 (0) | 2021.08.19 |